Kubernetes has come a long way over the last 2 years and I was so excited to learn about during CloudNativeCon/Kubecon Berlin this year.
As of Today Kops the standard tool for installing Kubernetes on AWS doesn’t support GCP yet (it’s in the works). However you can still setup your cluster using good old kube-up.sh. There’s also a pretty good explanation on the k8s docs. Make sure you install the Google Cloud SDK with gcloud and all their utils.
First download the kube tar.gz release of your choice from here: https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/releases. For example:
curl -0 https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/releases/download/v1.6.3/kubernetes.tar.gz | tar -zx
Then go to the kubernetes/cluster/gce directory. You’ll see a bunch of files there:
$ ls
BUILD config-test.sh cos gci upgrade.sh
config-common.sh configure-vm.sh debian list-resources.sh util.sh
config-default.sh container-linux delete-stranded-load-balancers.sh OWNERS
The file you’ll want to change is config-default.sh. I mofified mine like this (just a couple of changes):
# Copyright 2014 The Kubernetes Authors.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# TODO(jbeda): Provide a way to override project
# gcloud multiplexing for shared GCE/GKE tests.
KUBE_ROOT=$(dirname "${BASH_SOURCE}")/../..
source "${KUBE_ROOT}/cluster/gce/config-common.sh"
GCLOUD=gcloud
ZONE=${KUBE_GCE_ZONE:-us-central1-b}
REGION=${ZONE%-*}
RELEASE_REGION_FALLBACK=${RELEASE_REGION_FALLBACK:-false}
REGIONAL_KUBE_ADDONS=${REGIONAL_KUBE_ADDONS:-true}
NODE_SIZE=${NODE_SIZE:-n1-standard-1} # <- HERE
NUM_NODES=${NUM_NODES:-2} # <- HERE
MASTER_SIZE=${MASTER_SIZE:-n1-standard-$(get-master-size)}
MASTER_DISK_TYPE=pd-ssd
MASTER_DISK_SIZE=${MASTER_DISK_SIZE:-20GB}
NODE_DISK_TYPE=${NODE_DISK_TYPE:-pd-standard}
NODE_DISK_SIZE=${NODE_DISK_SIZE:-100GB}
REGISTER_MASTER_KUBELET=${REGISTER_MASTER:-true}
PREEMPTIBLE_NODE=${PREEMPTIBLE_NODE:-false}
PREEMPTIBLE_MASTER=${PREEMPTIBLE_MASTER:-false}
KUBE_DELETE_NODES=${KUBE_DELETE_NODES:-true}
KUBE_DELETE_NETWORK=${KUBE_DELETE_NETWORK:-false}
...
Then:
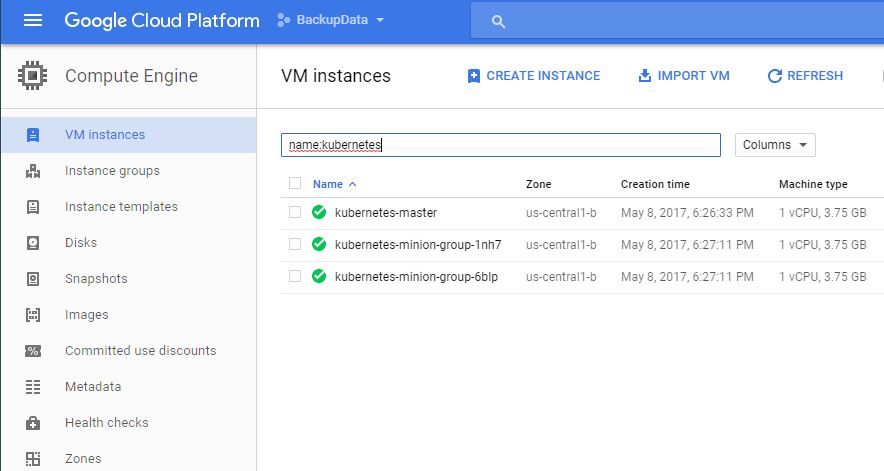
$ cd kubernetes/cluster && ./kube-up.sh
and voilà:
Then you can install kubectl (Cube Cuttle). The config will already be setup by kube-up.sh. But you can inspect if if you like under ~/.kube/
gcloud components install kubectl
After that you can do all the good stuff, like run apps: kubectl run <app> or create/expose services kubectl expose svc <service-name>, etc.
$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
hello-world-4125299140-gk334 1/1 Running 0 3d
hello-world-4125299140-hpcr3 1/1 Running 0 3d
hello-world-4125299140-j3nd7 1/1 Running 0 3d
jittery-platypus-mysql-3943010769-pbq45 1/1 Running 0 2d
my-nginx-858393261-fgjzl 1/1 Running 0 2d
my-nginx-858393261-s49dl 1/1 Running 0 2d
$ kubectl get svc
NAME CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
hello-world-4125299140 10.0.177.91 104.155.161.3 80:32569/TCP 3d
jittery-platypus-mysql 10.0.123.233 <none> 3306/TCP 2d
kubernetes 10.0.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 5d
my-nginx 10.0.190.149 <none> 80/TCP 4d
my-nginx-858393261 10.0.129.225 35.188.28.43 80:31120/TCP 4d